Technical Information(Product-Related Technical Materials)
See below for examples of technical information that will help you with the selection, design, and maintenance of each product.
Please create a free account or log in to our Technical Support Site to view other technical materials.
Make your ball screw last longer!
How to Apply Grease to a Ball Screw.
Why is it necessary to grease a ball screw?
To get the full performance from a ball screw, it is important that the rolling elements function properly.
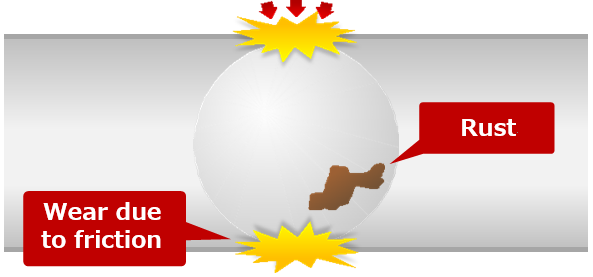
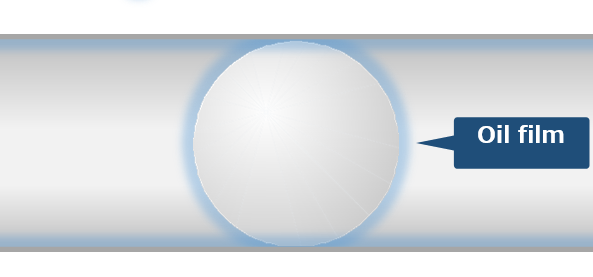
| Using a ball screw continuously without greasing it causes metal-to- metal contact. | When the ball screw is greased, the metal surfaces are covered with an oil film. |
 Enlarged view of ball screw rolling element |
 Enlarged view of ball screw rolling element |
| Growing friction of the rolling elements causes seizure and increased wear, leading to premature failure. | Grease reduces wear and heat generation and can also prevent rust. |
| It is essential to grease a ball screw to achieve and maintain its full performance! | |
|---|---|
| How to apply grease | |
|---|---|
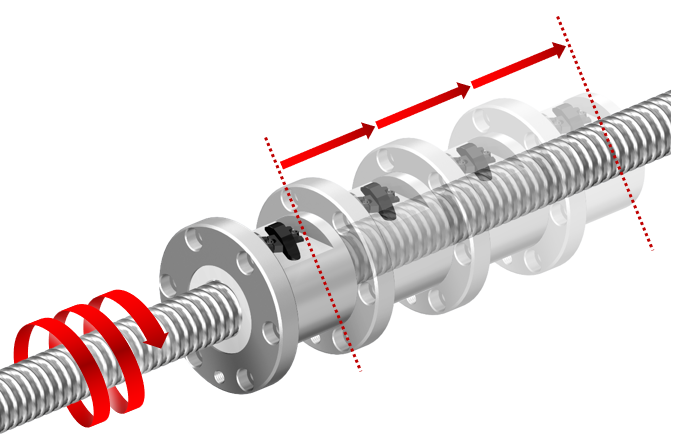
1/2 turn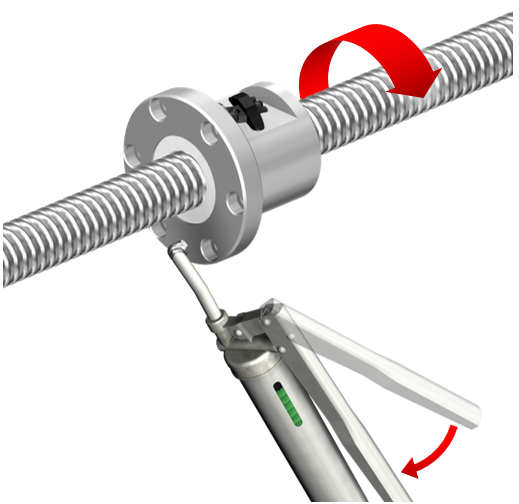 ※Grease gun:If 1 shot = 0.7 cm3 and the application amount is 7.0 cm3, apply 10 shots. |
Approx. 3 times
※If the effective thread length is less than 3 times the nut length, move it within the allowable stroke range. |
|
Apply the specified amount of grease, rotating the shaft by half a turn for each shot from the grease gun. |
After applying grease, move the nut by approximately three times the overall length of the nut so that the grease reaches the whole of the component. |
Caution
If you do not rotate the shaft while applying grease, the grease will run off of the seals, etc., and the specified amount will not be supplied to the nut.
Wipe off the grease that has come out, and re-apply the grease, following the application method.
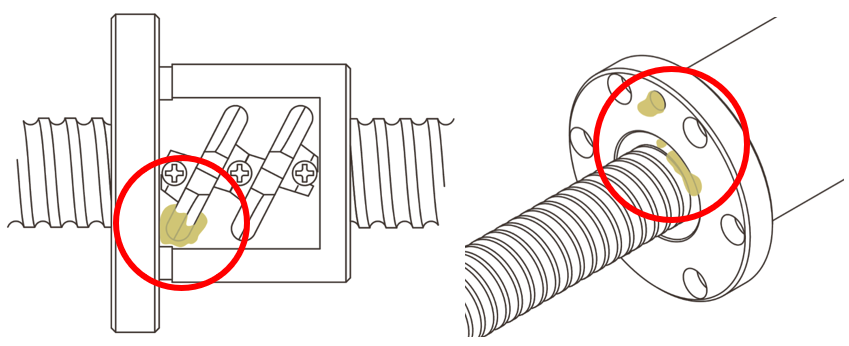
※Please contact THK regarding the amount of grease to apply.
How to select a representative LM Guide
The LM Guide has a wide variety
All models of the LM Guides looks similar at first glance...
By knowing the features of each model number, you can select the optimal model for your equipment.
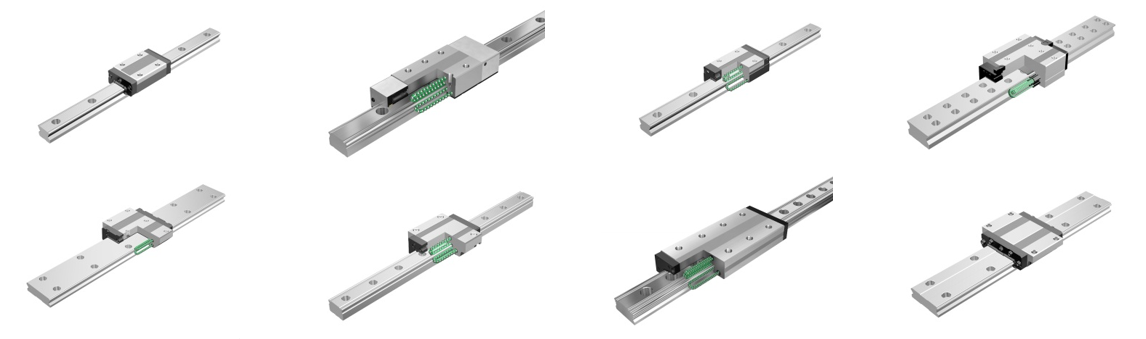
Here are 4 representative classifications that are frequently used.
| LM Guide-4 classifications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Caged Ball Type | Full-Ball Type (Without Ball Cage) |
|
| Radial type | SSR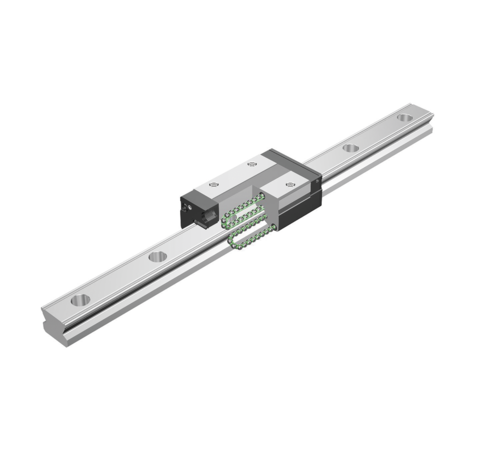
|
SR
|
| 4-way equal load type | SHS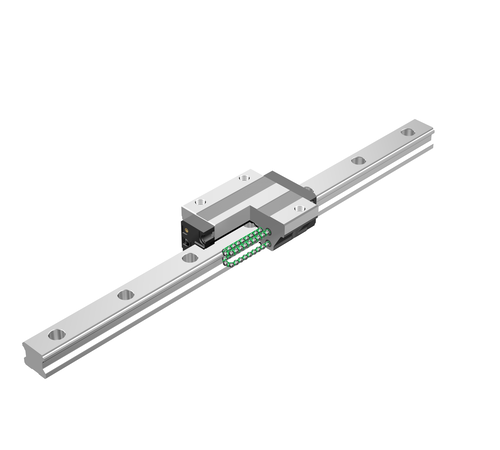 |
HSR |
Here are the “radial type” and “4-way equal load type,” whose structures differ greatly.
Depending on the direction of the applied load, you can select the most suitable one.
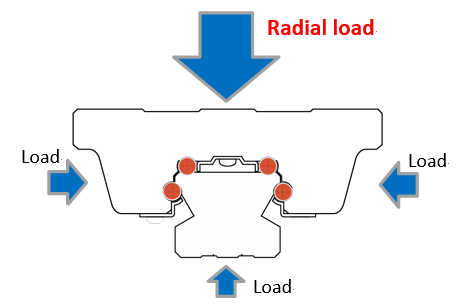
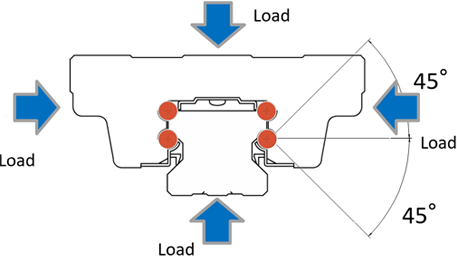
| Difference between "Radial type" and "4-way equal load" | |
|---|---|
| Radial type | 4-way equal load type |
|
 |
This type is strong against loads from above. It is most suitable for horizontal use, which is the most popular mounting orientation for the LM Guide.
 |
This type has equal load capacity from all directions. For this reason, it is suitable for vertical and wall mount use.
|
| Representative models Caged Ball Type:SSR Full-Ball Type (Without Ball Cage):SR |
Representative models Caged Ball Type:SHS Full-Ball Type (Without Ball Cage):HSR |